Swing trading is a popular trading strategy among beginners and experienced traders alike, known for its flexibility and potential for profits over short to medium time frames. Unlike day trading, which involves making multiple trades in a single day, swing trading focuses on capturing market “swings” that occur over several days or weeks. This approach allows traders to take advantage of short-term market movements without the intense pressure of minute-to-minute decision-making.
If you’re a beginner looking to dive into swing trading, this article will walk you through the fundamental strategies to get started and build a solid foundation for success.
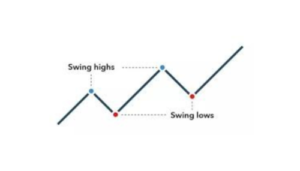
What is Swing Trading?
Swing trading involves holding positions for a few days to a few weeks to capture price changes or “swings” in the market. Traders using this approach aim to profit from short-term price movements and trends. Swing traders typically rely on technical analysis, using tools like charts, indicators, and patterns to make their trading decisions.
One of the main advantages of swing trading is that it doesn’t require constant monitoring of the markets, making it suitable for those with full-time jobs or other commitments. However, success still depends on careful analysis and a disciplined strategy.
Essential Swing Trading Strategies for Beginners
1. Trend Trading
One of the most straightforward swing trading strategies is trend trading. This method involves identifying a market trend and then “riding the wave” of that trend. If the market is in an uptrend (higher highs and higher lows), swing traders look for opportunities to buy into the trend. Conversely, during a downtrend (lower highs and lower lows), traders may seek opportunities to short the market.
How to Apply Trend Trading:
- Use trendlines and moving averages (e.g., the 50-day and 200-day moving averages) to identify the trend.
- Enter the trade when the price moves back in the direction of the trend after a pullback.
- Set stop losses below support levels in uptrends and above resistance levels in downtrends.
2. Breakout Trading
Breakout trading focuses on entering the market when the price breaks through a key level of support or resistance. These breakouts often signal the beginning of a new trend or a significant price movement, offering lucrative opportunities for swing traders.
How to Apply Breakout Trading:
- Identify strong support and resistance levels on the chart.
- Wait for the price to close above resistance for a bullish breakout or below support for a bearish breakout.
- Confirm the breakout using indicators such as the relative strength index (RSI) or volume spikes, which indicate momentum behind the breakout.
3. Reversal Trading
Reversal trading seeks to capture a change in the market’s direction. Traders using this strategy look for points where the current trend is likely to reverse, either from an uptrend to a downtrend or vice versa. Catching a trend reversal early can lead to significant profits, though this strategy can be riskier than trend-following.
How to Apply Reversal Trading:
- Use tools like RSI or moving average convergence divergence (MACD) to spot overbought or oversold conditions, which often signal potential reversals.
- Look for candlestick patterns such as dojis or engulfing patterns, which often indicate a change in trend.
- Be cautious of false signals; it’s crucial to wait for confirmation before entering the trade.
4. Range Trading
In markets where prices are moving sideways rather than trending, swing traders often employ range trading. This strategy involves buying at the lower end of the price range (support) and selling at the upper end (resistance), capitalizing on the oscillations within a defined range.
How to Apply Range Trading:
- Identify horizontal support and resistance levels where the price consistently bounces.
- Buy when the price approaches the support level and sell as it nears the resistance level.
- Set stop losses slightly below the support level to limit potential losses if the price breaks down.
5. Using Moving Averages for Swing Trading
Moving averages are a vital part of swing trading strategies. The 50-day and 200-day moving averages are two commonly used tools that help traders identify both the direction and strength of the trend. When the short-term moving average crosses above the long-term moving average, it’s considered a bullish signal. The reverse is true for bearish signals.
How to Use Moving Averages:
- Look for crossover points, such as the golden cross (50-day moving average crossing above the 200-day moving average) and the death cross (50-day crossing below the 200-day).
- Use moving averages in combination with other indicators to confirm trends and reversals.
Risk Management in Swing Trading
For beginners, managing risk is as important as finding the right strategies. Swing trading involves holding positions for days or weeks, and markets can be unpredictable. To minimize risk, always set stop-loss orders to protect your capital. Risk only a small percentage of your total trading capital on each trade, typically 1-2%. This way, even if a trade goes against you, it won’t wipe out your account.
It’s also crucial to stay patient and avoid emotional trading. Beginners often make the mistake of overtrading or holding onto losing trades too long in the hopes that the market will reverse. Establish a trading plan and stick to it, using a disciplined approach for both entry and exit points.
Final Thoughts
Swing trading offers a flexible and potentially profitable approach to trading for beginners. By learning essential strategies like trend trading, breakout trading, reversal trading, and range trading, new traders can build a solid foundation for success. It’s important to remember that swing trading requires patience, discipline, and a commitment to ongoing learning and market analysis.
As you gain experience, fine-tune your strategies and adapt to different market conditions. With practice and the right mindset, swing trading can become a rewarding part of your financial journey.